Before you send an email newsletter to the contacts stored in your Yahoo address book, you need to export the contacts from your Yahoo account to a common CSV file and import them into your email marketing software. To export Yahoo contacts to a CSV…
Yahoo Delivery Issues: Why Email is Placed to the Spam Folder
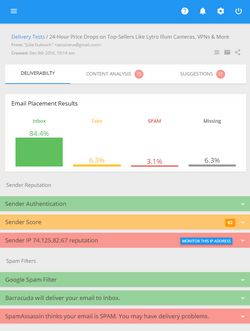
We’re receiving emails from our customers who complain of having troubles with delivering their messages to Yahoo email addresses. Despite correctly setup email authentication records (DKIM, SPF and DMARC) emails are often moved to the Yahoo’s spam folder.
Deliverability is a real challenge in the modern email marketing as spam filters are constantly evolving and filtering incoming mail more aggressively than ever. Yahoo is not an exception.
In this article, we tell about the key factors the Yahoo mailbox provider uses to determine if an email message is spam or not and give tips senders can implement to improve deliverability to their Yahoo users.
So, the key factors Yahoo looks at when deciding whether or not a message is spam are:
#1. IP Address Reputation.
When you are using an email service provider (ESP), as a rule, you share the sending IPs with other ESP customers. In this scenario, the IP reputation is built based on the mailing activity of all users. ESP usually use a pool of IP addresses that they rotate during message sending. Sometimes some IP in the pool can end up on blacklists which may affect deliverability, but ESP used to solve the IP blacklisting issues in a timely manner. That means you do need to worry about it. If you are concerned about your deliverability, you can ask the email service provider to provide you with a dedicated IP where you will be able to build your own reputation.
Be careful about new IPs. If your IP address is rather new or if you have not sent a lot of emails from it yet, the IP has little or no existing reputation. It is OK if you do not start blasting big email campaigns one day.
If you do, your IP would look like a machine compromised by a spammer and raise a “red flag” to email filtering systems and ISPs. The consequences can include the downgrade of your server’s reputation and blacklisting.
To protect your new IP address, take the time to “warm it up.” Start by sending small blasts of a few thousand messages at a time and slowly increase the volume over a few weeks. This way, you’ll introduce your new sending IP address to the Internet world in a smooth and safe way that spam filtering services will appreciate.
Although Yahoo doesn’t have an IP whitelisting program to guarantee the Inbox deliverability, senders can submit their IPs for review.
Based on their review, they will modify your reputation in their systems if needed. But you should keep in mind that it still doesn’t guarantee the Inbox deliverability.
#2. Domain Reputation.
Spam filters create lists of suspicious domains based on emails they have previously filtered. If you or other people using the same email or domain were previously sending spam, your emails could be seen as more suspicious by spam filters.
Nowadays, more and more mailbox providers are switching to the domain reputation.
Like Gmail, Yahoo started relying on the sender’s domain reputation.
If the spam test you do with GlockApps or other tool does not reveal any issues with your sending IP, authentication, and email content, but your email is still filtered as spam at Yahoo, you can consider setting up a new domain and build a new reputation for it to get your emails delivered.
Register a new domain using your brand, for example, brandmail.com, set up a new sending address, and begin using best practices to achieve good engagement and reputation.
A consistent sending from the same domain builds trust with your recipients, increases engagement, which will help your deliverability rate.
#3. Sender Reputation.
The sender reputation is a much broader notion than the IP and domain reputation. Besides these factors, it includes spam complaints, spam trap hits, bounce rate, and recipient engagement.
Even if you have a reputable sending history, recipients can report your email as spam and affect your overall reputation. So, if you want to get your emails to the Inbox, the best practice is to send relevant content to the people who want it and have opted to receive it.
#4. URL Reputation.
Links that you use in your message do matter for email placement. It’s important to ensure that the domains in the links are not listed in spam databases.
It’s also important that the domain in the destination URL matches the domain in the visible URL. If the domains do not match, spam filters consider it as a phishing practice. You may want to use an anchor text for the URL to avoid such an issue.
#5. DKIM Signatures.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an open, DNS-based email authentication standard that uses public key encryption to authenticate email messages. DKIM is used to ensure that the message has not been altered in transmission.
Major mailbox providers including Yahoo look at the DKIM email authentication when delivering the email. If the message passes the DKIM authentication, it has more chances to be delivered to the recipient’s Inbox.
#6. DMARC Authentication.
DMARC, an industry consortium to promote safer email and reduce spoofing, is supported by Yahoo. If a sender publishes a DMARC policy, Yahoo will honor it.
DMARC allows senders to specify how receivers can act on email which may not be sent from their domains. Depending on the policy published by the sender it may get rejected, or go to the spam folder or no action may be taken.
Yahoo also publishes a DMARC policy as a sender that guides receivers to reject email that may not be legitimately sent by Yahoo.
#7. Autonomous System Number (ASN) Reputation.
Autonomous System Number (ASN) is a globally unique number that is assigned to a group of IP networks operated by one or more network operators. Think of an ASN as having a unique number assigned to your neighborhood. Your neighborhood would build a reputation based on the people who live there and what types of emails they send.
How to Improve Deliverability to the Yahoo Users
Yahoo suggests a number of actions senders can take to improve deliverability to their Yahoo recipients:
– use confirmed opt-in process to build an email list
– send relevant messages
– be consistent with your mailings
– use separate IP addresses for different types of content (for example, separate transactional and marketing mail streams and send them from different IPs)
– pay attention to the subject lines because the recipients will make a decision based on them and if messages are being deleted without being read, that will hurt your sending reputation
– remove bounce and unsubscribed emails from future mailings
– signup for the Yahoo Complaint Feedback Loop to be notified about complaints and unsubscribe users who have marked your message as spam
– implement the DKIM and DMARC authentication for your domain
– set up reverse DNS (PTR) records for your sending IPs because Yahoo is more likely to downgrade the IP’s sending reputation if there isn’t a reverse DNS entry for your IP address
– monitor your sender reputation using spam testing tools like GlockApps